Data Portal
Setting up your data portal involves configuring and running Elasticsearch, Maestro, Arranger and Stage. Below are the steps and breakdowns to ensure a smooth setup process.
Setting up Elasticsearch
-
Run Elasticsearch: Use the following command to pull and run the Elasticsearch docker container
docker run -d --name elasticsearch \
-p 9200:9200 \
-e discovery.type=single-node \
-e cluster.name=workflow.elasticsearch \
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx2048m" \
-e ELASTIC_PASSWORD=myelasticpassword \
-e xpack.security.enabled=true \
-e MANAGE_INDEX_TEMPLATES=true \
-e NETWORK_HOST=http://localhost:9200 \
docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.1Click here for a detailed breakdown
-
-p 9200:9200maps port 9200 of the host to port 9200 of the container -
-e discovery.type=single-nodeconfigures Elasticsearch to run in single-node mode, this bypasses the need for cluster discovery and formation protocols, making Elasticsearch start up as a standalone node, ideal for development, testing, or small-scale deployments where clustering is not necessary -
-e cluster.name=workflow.elasticsearchnames the Elasticsearch cluster, this is good practice in case you choose to run multiple clusters or nodes in the future -
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx2048msets the initial and maximum heap size for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) running Elasticsearch.-Xms512msets the initial heap size to 512 MB.-Xmx2048msets the maximum heap size to 2048 MB (2 GB). Properly setting these values ensures that Elasticsearch has enough memory to handle its operations efficiently, but not so much that it starves other processes on the host machine. -
-e xpack.security.enabled=trueactivates security features such as authentication, authorization, encryption, and audit logging -
-e MANAGE_INDEX_TEMPLATES=trueensures Elasticsearch manages index templates, when true, the system expects to manage the index templates as part of its operations. In the next step we will create a client services to set up the default configurations for new indices -
-e ELASTIC_PASSWORD=myelasticpasswordSets the password for the elastic user
We use Elasticsearch 7Our search platform is built on and compatible with version 7.x of Elasticsearch. Applications and queries need to follow Elasticsearch 7 syntax and conventions.
-
Would you like me to explain any specific Elasticsearch 7 features or compatibility considerations in more detail?
-
Supply an index template: Create a folder titled
elasticsearchConfigsDownload and place the following quickstart_index_template.json within your
elasticsearchConfigsfolder. This file specifies settings, mappings, and configurations that will be applied automatically to new indices that match the template's patternLearn MoreIf you'd like to learn more about creating an index mapping for your own data see our administration guide on configuring the index mapping.
-
Initialize your index: Run the following scripts to set up your Elasticsearch cluster
Update Elasticsearch with your index template using the following
curlcommand:curl -u elastic:myelasticpassword -X PUT 'http://localhost:9200/_template/index_template' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ./elasticsearchConfigs/quickstart_index_template.jsonCreate a new alias in Elasticsearch using the following
curlcommand:curl -u elastic:myelasticpassword -X PUT 'http://localhost:9200/overture-quickstart-index'If successful you should be able to view the updated index in your browser from
http://localhost:9200/overture-quickstart-indexwith the usernameelasticand passwordmyelasticpassword.How this worksAny index alias that starts with
overture-will use the mapping of the index template we initially provided. This is defined on line two of ourquickstart_index_template.
Running Maestro
-
Create an env file: Create a file named
.env.maestrowith the following content:# ==============================
# Maestro Environment Variables
# ==============================
# Maestro Variables
MAESTRO_FAILURELOG_ENABLED=true
MAESTRO_FAILURELOG_DIR=app/logs/maestro
MAESTRO_LOGGING_LEVEL_ROOT=INFO
MAESTRO_NOTIFICATIONS_SLACK_ENABLED=false
# Song Variables
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_CODE=song.overture
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_URL=http://song:8080
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_NAME=Overture
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_ORGANIZATION=Overture
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_COUNTRY=CA
# Elasticsearch Variables
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLUSTER_NODES=http://elasticsearch:9200
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLIENT_BASICAUTH_USER=elastic
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLIENT_BASICAUTH_PASSWORD=myelasticpassword
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLIENT_TRUSTSELFSIGNCERT=true
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_INDEXES_ANALYSISCENTRIC_ENABLED=false
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_INDEXES_FILECENTRIC_ENABLED=true
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_INDEXES_FILECENTRIC_NAME=overture-quickstart-index
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_INDEXES_FILECENTRIC_ALIAS=file_centric
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLIENT_BASICAUTH_ENABLED=true
MANAGEMENT_HEALTH_ELASTICSEARCH_ENABLED=false
# Spring Variables
SPRING_MVC_ASYNC_REQUESTTIMEOUT=-1
SPRINGDOC_SWAGGERUI_PATH=/swagger-api
# Kafka Variables
SPRING_CLOUD_STREAM_KAFKA_BINDER_BROKERS=kafka:9092
SPRING_CLOUD_STREAM_BINDINGS_SONGINPUT_DESTINATION=song-analysisClick here for a detailed breakdown
Maestro Variables
-
MAESTRO_FAILURELOG_ENABLEDenables or disables failure logging. When set totrue, Maestro logs any failures that occur, which is useful for debugging and monitoring purposes -
MAESTRO_FAILURELOG_DIRsets the directory path where failure logs are stored. The value should beapp/logs/maestroor another path of your choosing -
MAESTRO_LOGGING_LEVEL_ROOTsets the root logging level for Maestro. The value can beINFO,DEBUGorWARN. It determines the level of detail included in logs, whereINFOis standard andDEBUGprovides more detailed information -
MAESTRO_NOTIFICATIONS_SLACK_ENABLEDenables or disables Slack notifications. When set totrue, Maestro can send notifications to a Slack channel
Song Variables
-
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_CODEsets the code identifier for the repository. The value here issong.overture, serving as a unique identifier used within Maestro to reference the repository -
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_URLis the URL of the metadata repository. The value ishttp://song:8080, specifying the endpoint where Maestro can connect to the Song repository -
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_NAMEdefines the display name for the repository. The value isOverture, providing a human-readable name for the repository used in logs and interfaces -
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_ORGANIZATIONdefines the name of the organization that owns the repository -
MAESTRO_REPOSITORIES_0_COUNTRYdefines the country code for the repository's location. The value isCA(Canada), indicating the country associated with the repository
Elasticsearch Variables
-
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_INDEXES_ANALYSISCENTRIC_ENABLEDset totruespecifying that analysis-centric indices are to be expected -
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_INDEXES_FILECENTRIC_ENABLEDset tofalsespecifying to Maestro that file-centric indices are not to be expected -
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLIENT_BASICAUTH_ENABLEDenables basic authentication for the Elasticsearch client -
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_INDEXES_ANALYSISCENTRIC_NAMEis the name of the analysis-centric Elasticsearch index. The value isanalysis-composer-index, aligned with our previously created index -
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_INDEXES_ANALYSISCENTRIC_ALIASis the alias for the analysis-centric Elasticsearch index -
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLUSTER_NODESpoints to the address of the Elasticsearch cluster node(s). The value iselasticsearch:9200, specifying the Elasticsearch node that Maestro will interact with -
MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLIENT_BASICAUTH_USER,MAESTRO_ELASTICSEARCH_CLIENT_BASICAUTH_PASSWORDis the username and password for Elasticsearch -
MANAGEMENT_HEALTH_ELASTICSEARCH_ENABLED: Enables or disables Elasticsearch health checks. The value can befalse(disabled) ortrue(enabled), controlling whether health checks for Elasticsearch are performed. -
MANAGEMENT_SECURITY_ENABLED: Enables or disables security management. The value can befalse(disabled) ortrue(enabled), controlling whether security features are enabled.
Spring Variables
-
SPRING_MVC_ASYNC_REQUESTTIMEOUTis-1(no timeout), this setting determines how long asynchronous requests are allowed to run before timing out -
SPRINGDOC_SWAGGERUI_PATHis/swagger-api, specifying the URL path where the Swagger UI can be accessed (localhost:11235/swagger-api).
Kafka Variables
-
SPRING_CLOUD_STREAM_KAFKA_BINDER_BROKERSdefines the address of the Kafka broker(s). The value is set tokafka:9092, specifying the Kafka instance we set up earlier -
SPRING_CLOUD_STREAM_BINDINGS_SONGINPUT_DESTINATIONis the destination topic for the Song input binding. The value issong-analysis, pointing to the Kafka topic we configured earlier
-
-
Run Maestro: Use the docker run command with the
--env-fileoption:docker run --env-file .env.maestro \
--name maestro \
--platform linux/amd64 \
-p 11235:11235 \
ghcr.io/overture-stack/maestro:4.3.0
Running Arranger
-
Create an env file: Create a file named
.env.arrangerwith the following content:# ==============================
# Arranger Environment Variables
# ==============================
# Arranger Variables
ENABLE_LOGS=false
# Elasticsearch Variables
ES_HOST=http://elasticsearch:9200
ES_USER=elastic
ES_PASS=myelasticpassword
# Stage Variables
REACT_APP_BASE_URL=http://stage:3000
REACT_APP_ARRANGER_ADMIN_ROOT=http://arranger-server:5050/graphql -
Create a folder titled
arrangerConfigsand place the following configuration files within it:- The base.json, containing the base configuration for the Arranger server
- The extended.json, containing all possible fields inputted into arranger
- The facets.json, defines the facets found within the facet panel of the data exploration page in Stage
- The matchbox.json, containing matchbox configuration settings
- The table.json, defines the formatting of the tables found on the data exploration page in Stage
-
Run Arranger: Use the docker run command with your
.env.arrangerfile:docker run --env-file .env.arranger \
--name arranger-server \
-p 5050:5050 \
-v ./arrangerConfigs/base.json:/app/modules/server/configs/base.json \
-v ./arrangerConfigs/extended.json:/app/modules/server/configs/extended.json \
-v ./arrangerConfigs/facets.json:/app/modules/server/configs/facets.json \
-v ./arrangerConfigs/matchbox.json:/app/modules/server/configs/matchbox.json \
-v ./arrangerConfigs/table.json:/app/modules/server/configs/table.json \
ghcr.io/overture-stack/arranger-server:3.0.0-beta.33Make sure to confirm the
./arrangerConfigs/path aligns with the actual paths to your Arranger-Server configuration files, update your command or folder structure accordingly.Click here for a detailed breakdown
When creating the .env.arranger file:
-
ES_HOSTis the URL of your Elasticsearch instance -
ES_USERandES_PASSare the credentials for accessing Elasticsearch -
REACT_APP_BASE_URLis the base URL for your front-end application, in this case Stage, which we will set up next -
REACT_APP_ARRANGER_ADMIN_ROOTis the URL for the Arranger GraphQL endpoint
When running Arranger:
-
-p 5050:5050maps port 5050 of the host to port 5050 of the container. -
-v ./arrangerConfigs/...:/app/modules/server/configs/...mounts configuration files into the containerbase.jsoncontains the base configuration for the Arranger serverextended.jsoncontains all possible fields inputted into arrangerfacets.jsondefines the facets found within the facet panel of the data exploration page in Stagetable.jsondefines the formatting of the tables found on the data exploration page in Stagematchbox.jsoncontains matchbox configuration settings
Configuring ArrangerIf you want to learn more about configuring Arranger see our administration guide on customizing the search portal.
-
Setting up Stage
-
Create an env file: Create a file named
.env.stagewith the following content:# ==============================
# Stage Environment Variables
# ==============================
# Stage Variables
NEXTAUTH_URL=http://localhost:3000/api/auth
NEXT_PUBLIC_LAB_NAME=Overture QuickStart Portal
NEXT_PUBLIC_ADMIN_EMAIL=contact@overture.bio
NEXT_PUBLIC_DEBUG=true
NEXT_PUBLIC_SHOW_MOBILE_WARNING=true
# Keycloak Variables
NEXT_PUBLIC_AUTH_PROVIDER=keycloak
ACCESSTOKEN_ENCRYPTION_SECRET=super_secret
SESSION_ENCRYPTION_SECRET=this_is_a_super_secret_secret
NEXT_PUBLIC_KEYCLOAK_HOST=http://keycloak:8080
NEXT_PUBLIC_KEYCLOAK_REALM=myrealm
NEXT_PUBLIC_KEYCLOAK_CLIENT_ID=webclient
KEYCLOAK_CLIENT_SECRET=ikksyrYaKX07acf4hpGrpKWcUGaFkEdM
NEXT_PUBLIC_KEYCLOAK_PERMISSION_AUDIENCE=dms
# Score Variables
NEXT_PUBLIC_SCORE_API_URL=http://score:8087
# Arranger Variables
NEXT_PUBLIC_ARRANGER_DOCUMENT_TYPE=file
NEXT_PUBLIC_ARRANGER_INDEX=file_centric
NEXT_PUBLIC_ARRANGER_API_URL=http://arranger-server:5050
NEXT_PUBLIC_ARRANGER_MANIFEST_COLUMNS=repositories.code, object_id, analysis.analysis_id, study_id, file_type, file.name, file.size, file.md5sum, file.index_file.object_id, donors.donor_id, donors.specimens.samples.sample_idClick here for a detailed breakdown
Stage Variables
-
NEXTAUTH_URLspecifies the base URL for NextAuth.js, which handles authentication in Next.js applications. This setting is used to configure the authentication flow, including where to redirect users after successful authentication. -
NEXT_PUBLIC_LAB_NAMEis the name that will be displayed in the top left of the portal interface. Feel free to get creative here -
NEXT_PUBLIC_ADMIN_EMAILis the email address of the administrator or support contact. This setting updates the help link found by default in the footer navigation of the portal interface
Keycloak Variables
-
NEXT_PUBLIC_AUTH_PROVIDERspecifies the authentication provider, in this case, Keycloak -
ACCESSTOKEN_ENCRYPTION_SECRETdefines the secret used to encrypt access tokens, enhancing security by preventing easy decoding of intercepted tokens -
SESSION_ENCRYPTION_SECRETspecifies the secret used to encrypt session cookies, protecting sensitive information stored in the cookie from unauthorized access -
NEXT_PUBLIC_KEYCLOAK_HOSTspecifies the URL where the Keycloak server is hostedhttps://localhost:8443whileNEXT_PUBLIC_KEYCLOAK_REALMdefines the realm in Keycloak that contains the users and roles for our application -
NEXT_PUBLIC_KEYCLOAK_CLIENT_IDand client secretKEYCLOAK_CLIENT_SECRETare assigned to the application by Keycloak, linking the application to its configuration within Keycloak -
NEXT_PUBLIC_KEYCLOAK_PERMISSION_AUDIENCEspecifies the audience for the permission claims in the access token, restricting the scope of access granted to the token
Score Variables
NEXT_PUBLIC_SCORE_API_URLis the URL of the Score API, which the application uses to communicate with the Score service
Arranger Variables
-
NEXT_PUBLIC_ARRANGER_DOCUMENT_TYPEindexes can be either file centric or analysis (participant) centric, the document type variable specifies which of these configurations is true -
NEXT_PUBLIC_ARRANGER_INDEXdefines the index used by the Arranger service -
NEXT_PUBLIC_ARRANGER_API_URLis the URL of the Arranger graphQL API, by default Arranger's API is mapped to port 5050 -
NEXT_PUBLIC_ARRANGER_MANIFEST_COLUMNSlists the columns to be included in the manifest generated for download with Score
-
-
Run Stage: Use the docker run command with your
.env.stagefile:docker run --env-file .env.stage \
--name stage \
-p 3000:3000 \
ghcr.io/overture-stack/stage:3ede4e2The front-end portal will now be available in your browser at
localhost:3000
Retrieving and updating access tokens
Now that we have our platform setup we will need to generate an API key to enable secure communication between Song and Score.
API Keys are brokered by Keycloak and accessible when logged in to the Stage UI localhost:3000/login.
-
Login through the Stage UI by selecting login from the top right.
Default credentials were pre-configured when we imported our Users.json file into Keycloak, our default admin account credentials are username
adminand passwordadmin123. -
Generate a new API token by selecting Profile and Token from your user dropdown menu at the top right of the Stage UI and selecting Generate New Token.
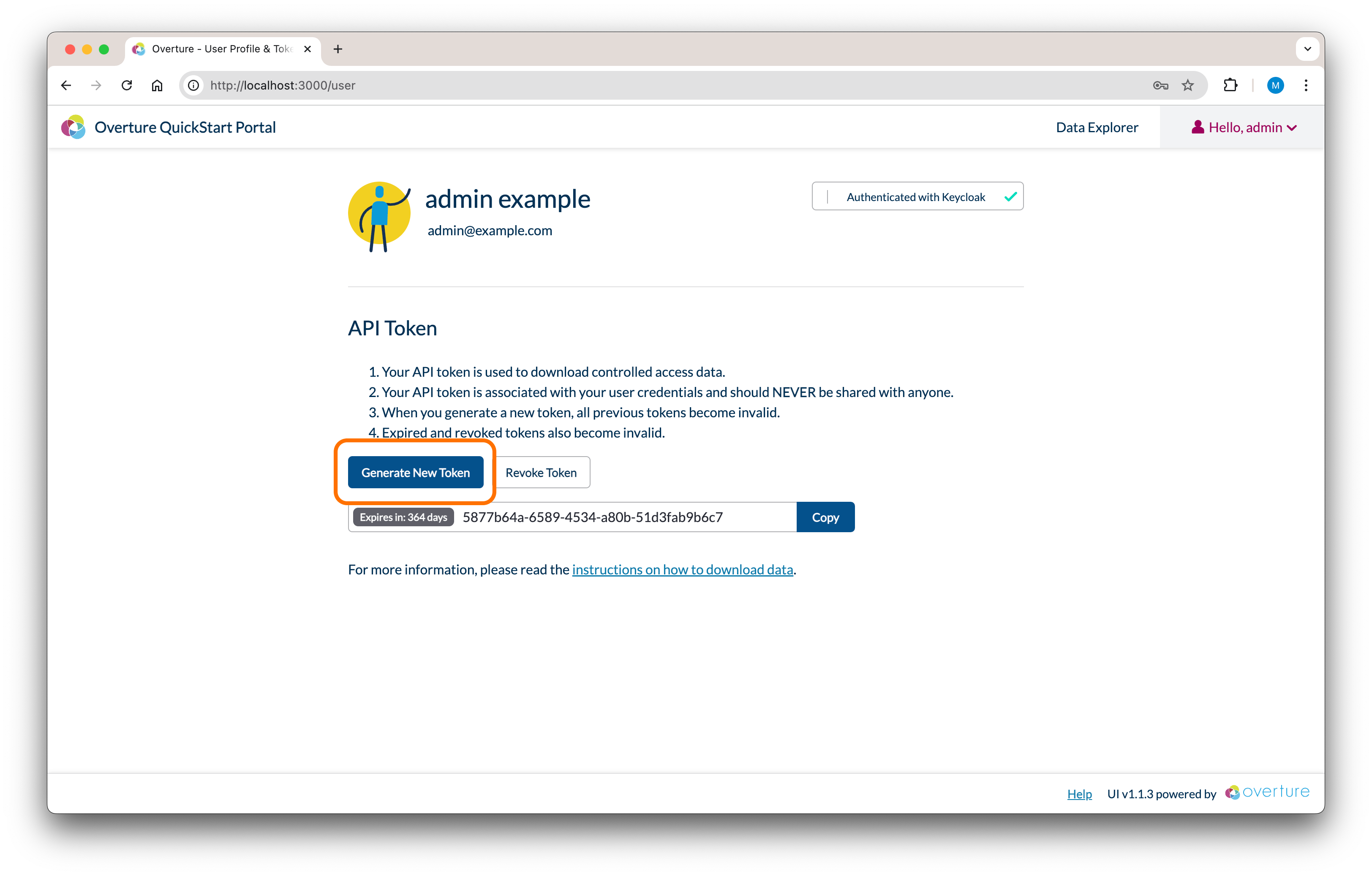
-
Update the
SCORE_ACCESSTOKENvariable within your.env.songand once updated, remove the existing Song container and re-run Song with your updated.env.songdocker run -d \
--name song \
--platform linux/amd64 \
-p 8080:8080 \
--env-file .env.song \
ghcr.io/overture-stack/song-server:438c2c42Next StepsNow that you have the end-to-end portal setup we recommend you check out our administration guide on updating the data model.